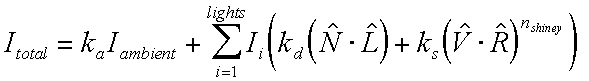Illumination and Shading
Computer Graphics Jargon:
-
Illumination - the transport of luminous flux from light sources between points via direct and indirect paths
-
Lighting - the process of computing the luminous intensity reflected from a specified 3-D point
-
Shading - the process of assigning a colors to a pixels
Illumination Models:
-
Empirical - simple formulations that approximate observed phenomenon
Java3D : Real Time illumination model : lots of approximations. No Shade, simplified transparency, no reflexion (miror).
-
Physically-based - models based on the actual physics of light's interactions with matter
Raytracing, Radiosity...
-
Local illumination model / Global illumination model
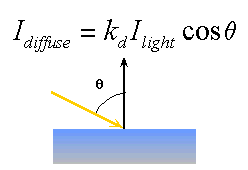
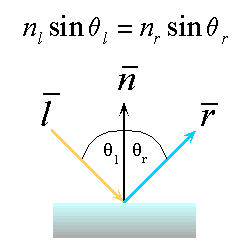 Reflection : a special case of the Snell / Descartes law
Reflection : a special case of the Snell / Descartes law