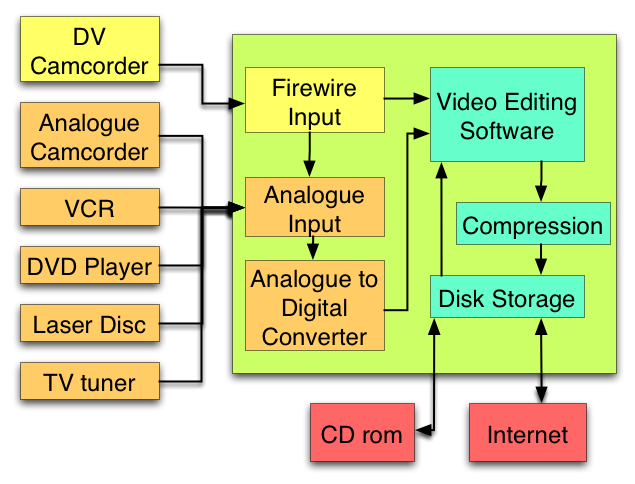
Video for The Web
For more about Pal/Secam vs NTSC : http://www.videointerchange.com/pal_secam_conversions.htm
For More about Digital Video and conversion issues (and the fact that pixels are often not square) : http://www.uwasa.fi/~f76998/video/conversion/
For More about Digital Video and Image Formats : http://www.zerocut.com/tech/vid_img.htm
The Best introduction to Digital Video for the Web : http://stream.uen.org/medsol/digvid/html/mainmenu.html
The Best introduction to Digital Video for the Web : http://stream.uen.org/medsol/digvid/html/mainmenu.html

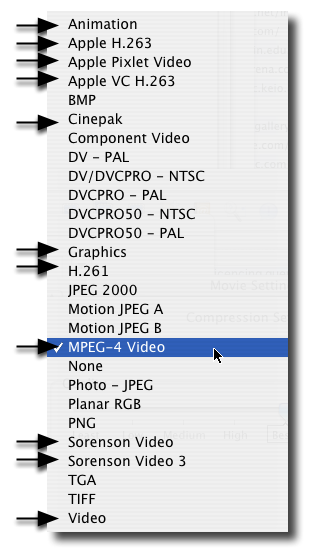
VIDEO
FORMATS
|
AUDIO
FORMATS
|
Source : http://stream.uen.org/medsol/digvid/html/5B_videoformats.html
For More : http://stream.uen.org/medsol/digvid/html/2B_mediaarchitecture.html
For More : http://www.discreet.com/support/codec/
The targeted codesc are designed for distribution
DV or MJPEG are are "Intermediate Codecs" |
 |
For More : http://www.synthetic-ap.com/qt/codec1.html
and http://www.synthetic-ap.com/qt/codec2.html
For More : their comparison http://home.earthlink.net/~mrob/pub/codecs.html
| The formats related to 625-line systems with a 50 Hz field rate | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sampling matrix | actual active picture size | supports interlacing |
notes | |||||
| width | height | width | height | |||||
| 768 | 576 | 767 | 576 | Y | "Industry standard" 625/50 square-pixel video | |||
| 768 | 576 | 768 | 576 | Y | "True" computer square-pixel resolution | |||
| 768 | 560 | 767 | 576 | Y | CD-i | |||
| 720 | 576 | 702 | 576 | Y | D1, DV, DVB, DVD, SVCD | |||
| 720 | 540 | 720 | 540 | N | Oddball compromise format. Better to avoid unless you really know what you are doing. | |||
| 704 | 576 | 702 | 576 | Y | DVD, H.263 (4CIF), VCD | |||
| 702 | 576 | 702 | 576 | Y | Active picture frame for 625/50 systems in ITU-R BT.601-4 pixels. | |||
| 544 | 576 | 526+1/2 | 576 | Y | DVB (3/4 of BT.601 sampling rate) | |||
| 480 | 576 | 468 | 576 | Y | SVCD (2/3 of BT.601 sampling rate) | |||
| 384 | 288 | 383+1/2 | 288 | N | 1/4 of "industry standard" 768576 | |||
| 384 | 280 | 383+1/2 | 288 | N | CD-i | |||
| 352 | 576 | 351 | 576 | Y | DVD | |||
| 352 | 288 | 351 | 288 | N | VCD, DVD, H.261 + H.263 (CIF) | |||
| 176 | 144 | 175+1/2 | 144 | N | H.261 + H.263 (QCIF) | |||
| The formats related to 525-line systems with a 59.94 Hz field rate | ||||||||
| sampling matrix | actual active picture size | supports interlacing |
notes | |||||
| width | height | width | height | |||||
| 720 | 540 | 720 | 540 | N | Oddball compromise format. Better to avoid unless you really know what you are doing. | |||
| 720 | 486 | 710.85 | 486 | Y | D1 | |||
| 720 | 480 | 710.85 | 486 | Y | DV, DVB, DVD, SVCD | |||
| 711 | 486 | 710.85 | 486 | Y | Active picture frame for 525/59.94 systems in ITU-R BT.601-4 pixels. | |||
| 704 | 486 | 710.85 | 486 | Y | ||||
| 704 | 480 | 710.85 | 486 | Y | ATSC, DVD, VCD | |||
| 648 | 486 | 648 | 486 | Y | "True" computer square-pixel resolution (all 486 active scanlines) | |||
| 640 | 480 | 646+5/22 | 486 | Y | D2: "industry standard" 525/59.94 square-pixel video | |||
| 640 | 480 | 648 | 486 | Y | "True" computer square-pixel format (cropped) | |||
| 480 | 480 | 473.9 | 486 | Y | SVCD (2/3 of BT.601 sampling rate) | |||
| 352 | 480 | 355.425 | 486 | Y | DVD | |||
| 352 | 240 | 355.425 | 243 | N | VCD, DVD | |||
| 320 | 240 | 324 | 243 | N | 1/4 of 640480 | |||
| 59.94 Hz is only a conventional approximation; the mathematically
exact field rate is
60 Hz * 1000/1001. A calculated sampling rate, represented here only for completeness. Does not exist in actual 525/625 video equipment. Only used for still images. |
||||||||
| Duration |
Data Rate |
Frame Size |
Frame Rate | File Size |
| 1 min | Uncompressed QuickTime 29.6 MBytes/sec |
720x480 | 29.97 fps interlaced |
1.8 GB/min |
| 1 min |
M-JPEG 7.4 MBytes/sec |
720x480 |
29.97fps interlaced |
450 MB/min |
| 1 min |
M-JPEG 1.8 MBytes/sec |
320x240 |
29.97fps de-interlaced |
110 MB/min |
|
1 min |
DV 3 MBytes/sec or 25 Mbits/sec |
720x480 |
29.97fps interlaced |
200 MB/min |
| 1 min |
QuickTime Sorenson 100 KBytes/sec (800 Kbits/sec) |
320x240 |
15fps de-interlaced |
5 MB/min |
| 1 min |
QuickTime Sorenson |
320x240 |
15fps de-interlaced |
1.7 MB/min |
| 1 min |
Quicktime Sorenson 56 Kbits/sec |
192x144 |
7.5fps de-interlaced |
0.5 MB/min |
| 1 min |
Quicktime Sorenson 28 Kbits/sec |
160x120 |
7.5fps de-interlaced |
220 KB/min |
| 1 min |
Real Media 97 kbits/sec |
240x180 |
10fps de-interlaced |
0.72 MB/min |
1 min |
Real Media 589 kbits/sec |
320x240 |
15fps de-interlaced |
4.25 MB/min |
1 min |
Real Media 2180 kbits/sec |
400x300 |
30fps de-interlaced |
15.4 MB/min |
1 min |
WindowsMedia v9 97 kbits/sec |
240x180 |
10fps de-interlaced |
0.78 MB/min |
1 min |
WindowsMedia v9 589 kbits/sec |
320x240 |
15fps de-interlaced |
4.1 MB/min |
1 min |
WindowsMedia v9 2176 kbits/sec |
400x300 |
30fps de-interlaced |
15.1 MB/min |
1 min |
MPEG-1 1383 kbits/sec |
320x240 |
30fps de-interlaced |
10.1 MB/min |
1 min |
MPEG-4 92 kbits/sec |
160x120 |
10fps de-interlaced |
0.71 MB/min |
1 min |
MPEG-4 565 kbits/sec |
320x240 |
15fps de-interlaced |
4.1 MB/min |
1 min |
MPEG-4 2088 kbits/sec |
640x480 |
30fps de-interlaced |
15.3 MB/min |
1 min |
DVD MPEG2 9180 kbits/sec or 8.96 Mbits/sec |
720x480 |
29.97fps interlaced |
80 MB/min CBR 11MB/min 3.2 MB/min |
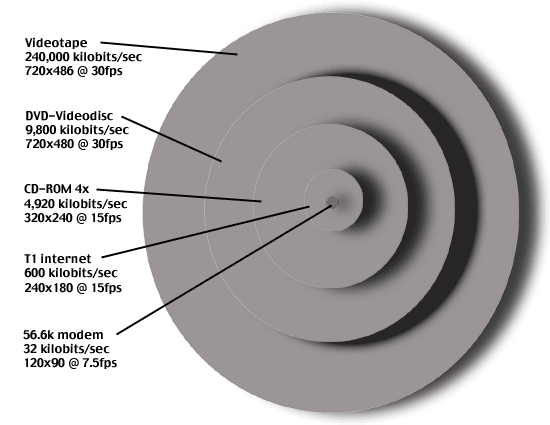
Source : http://stream.uen.org/medsol/digvid/html/3B_videoframerate.html
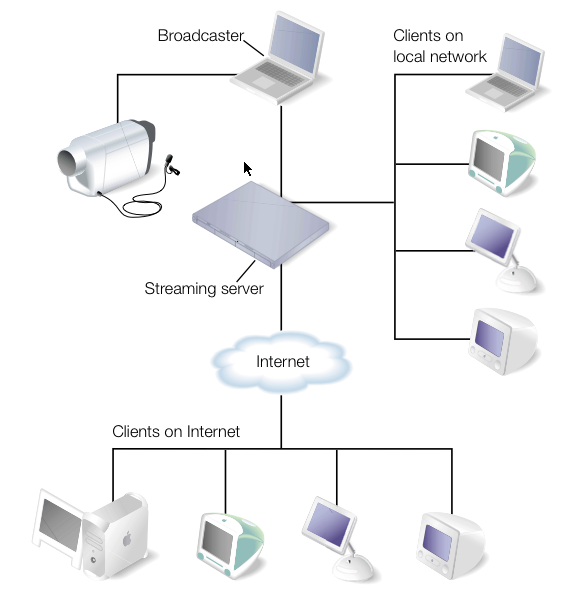
Video output |
Number of simultaneous connections |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mbps |
kbps |
1 |
2 |
5 |
10 |
40 |
100 |
200 |
1000 |
0.03 |
28.8 |
29 |
58 |
144 |
288 |
1152 |
3 |
6 |
29 |
0.05 |
54.0 |
54 |
108 |
270 |
540 |
2160 |
5 |
11 |
54 |
0.13 |
128.0 |
128 |
256 |
640 |
1280 |
5120 |
13 |
26 |
128 |
0.26 |
256.0 |
256 |
512 |
1280 |
2560 |
10240 |
26 |
51 |
256 |
0.38 |
384.0 |
0.4 |
0.8 |
2 |
4 |
15 |
38 |
77 |
384 |
0.51 |
512.0 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
3 |
5 |
20 |
51 |
102 |
512 |
1.02 |
1024.0 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
5 |
10 |
41 |
102 |
205 |
1024 |
2.25 |
2252.8 |
2 |
5 |
11 |
23 |
90 |
225 |
451 |
2253 |
4.10 |
4096.0 |
4 |
8 |
20 |
41 |
164 |
410 |
819 |
4096 |
8.19 |
8192.0 |
8 |
16 |
41 |
82 |
328 |
819 |
1638 |
8192 |
12.29 |
12288.0 |
12 |
25 |
61 |
123 |
492 |
1229 |
2458 |
12288 |
20.48 |
20480.0 |
20 |
41 |
102 |
205 |
819 |
2048 |
4096 |
20480 |
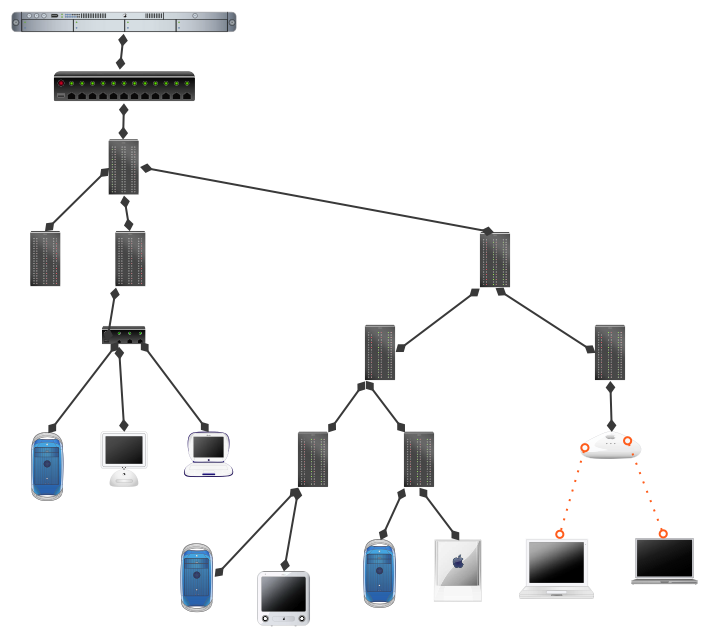
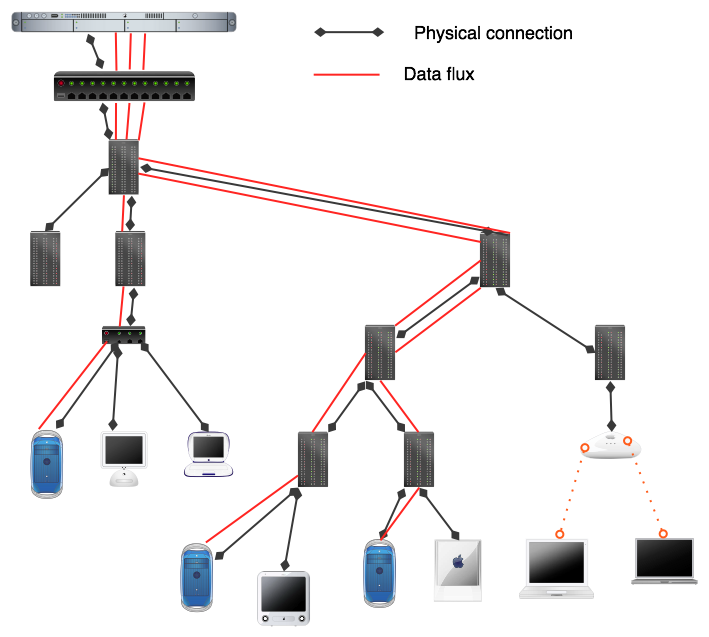
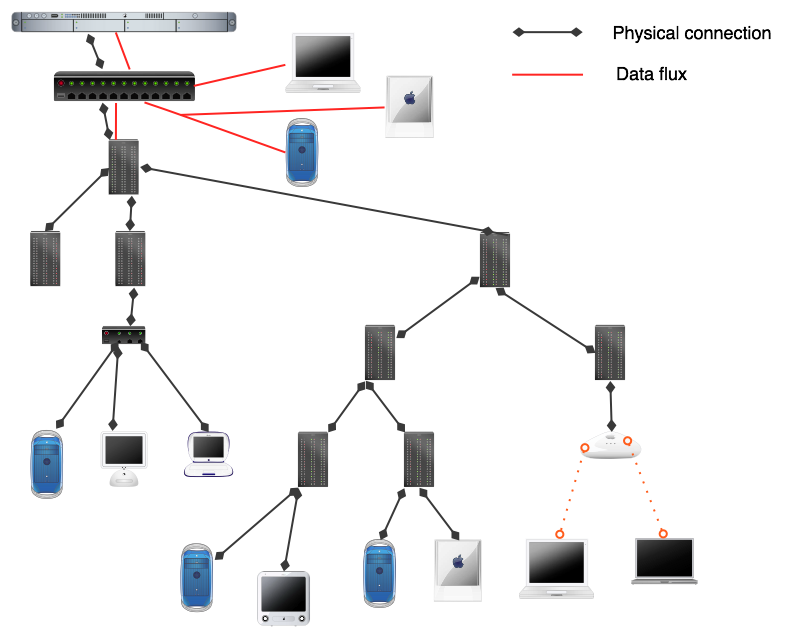
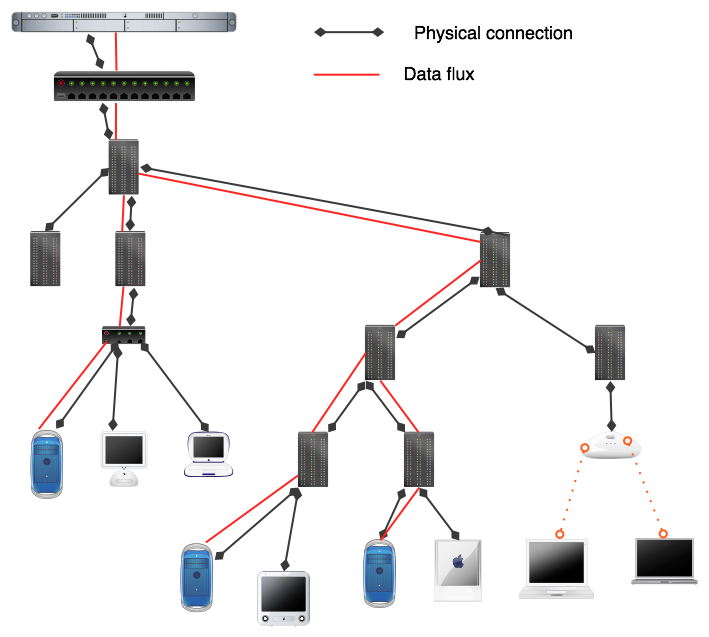
<OBJECT CLASSID="clsid:02BF25D5-8C17-4B23-BC80-D3488ABDDC6B" WIDTH="192" HEIGHT="160" CODEBASE="http://www.apple.com/qtactivex/qtplugin.cab"> <PARAM name="SRC" VALUE="video/extrait_2_qt_modem.mov"> <PARAM name="AUTOPLAY" VALUE="false"> <PARAM name="CONTROLLER" VALUE="true"> <PARAM name="SCALE" VALUE="aspect"> <EMBED src="video/extrait_2_qt_modem.mov" WIDTH="192" HEIGHT="160" SCALE="aspect" AUTOPLAY="false" CONTROLLER="true" LOOP="false" PLUGINSPAGE="http://www.apple.com/quicktime/download/" KIOSKMODE="false"> </EMBED> </OBJECT>
All the attributes : http://www.apple.com/quicktime/authoring/embed2.html
From Embed to Object : http://dopey.gcsu.edu/QT_embed_object_tags/
The width and height attributes of the object element should match the size of the movie in pixels.
The classid attribute uniquely identifies the player software to use. It must be set to "clsid:02BF25D5-8C17-4B23-BC80-D3488ABDDC6B". This unique code identifies an ActiveX control that must be installed on the users PC before the movie can be played. If the user does not have the ActiveX control installed, the browser can automatically download and install it.
The codebase attribute specifies the base path used to resolve relative URIs specified by the classid, data, and archive attributes. When absent, its default value is the base URI of the current document. Note: Internet Explorer uses this attribute to specify a location from where the player can be downloaded. It must be set to "http://www.apple.com/qtactivex/qtplugin.cab". This location will always contain the latest version of the QuickTime player.
The src parameter should point to the movie file.
The autoplay parameter should have the value "true" if you want the movie to play automatically.
The controller parameter should have the value "false" if you don't want the control buttons to show.
The embed element is added to support browsers that don't support the object element. A browser that understands the object element will ignore the embed element. The object element will be used by new browsers that support ActiveX controls (Internet Explorer 5 and 6). Older browsers (Netscape 4 and 5) will use the embed element.
The width and height attributes of the embed element should match the size of the movie in pixels.
The autoplay and controller attributes of the embed element should be set to the same values as for the parameters in the object element.
The pluginspage attribute defines the player's download path. It must be set to "http://www.apple.com/quicktime/download/".
http://www.apple.com/quicktime/tools_tips/tutorials/tracks.html
http://www.apple.com/quicktime/tools_tips/tutorials/hreftracks.html
and Examples : http://web.uvic.ca/akeller/pw408/d_qt_link_to_web_pages.html
http://www.apple.com/quicktime/tools_tips/tutorials/interactive.html
Creates alternate movies for various internet connection speeds, CPU's, languages, and more. This version runs on Mac OS X and allows you to create a reference movie that supports QuickTime 6.
http://developer.apple.com/quicktime/quicktimeintro/tools/
http://www.qtbridge.com/pageot/qtnext/Sequence_eng.html