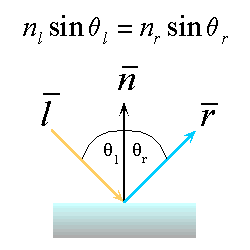Snell/Descartes's Law (1636 Snell discovers Descarte's laws...)
Reflection and Refraction behaves according to Snell's laws which state: One common PlaneThe incoming ray, the surface normal, and the reflected ray all lie in a common plane. One relation between angleThe angle that the reflected ray forms with the surface normal is determined by the angle that the incoming ray forms with the surface normal, and the relative speeds of light of the mediums in which the incident and reflected rays propogate according to the following expression. |
Reflection : a special case of the lawReflection is a very special case of Snell's Law where the incident light's medium and the reflected rays medium is the same. Thus we can simplify the expression to:
|
1620s: Snell and Descarte, Snell’s Law : http://www.geo.hunter.cuny.edu/~afrei/theory_of_light_lecture.htm
SNELL'S LAW (FROM DESCARTE'S DIOPTRICS, 1637) : http://bayes.cs.ucla.edu/LECTURE/lecture_sec1.htm
1636 Snell discovers Descarte's laws... : unix.temple.edu/~meziani/history.pdf
Snell deduced his law from experimental data and thought that cosecants fitted his data best. The frenchman Descarte was the first to use the correct sines. In France it is known as Descarte's Law! http://www.star.le.ac.uk/~rw/courses/lect220.html
4 REFRACTIVE INDEX
n = [(speed vacuum )/(speed medium
)] = [c/v]
It is a quantity that can be measured.
nglass = 1.52
nwater = 1.33
nair = 1.000292 at S.T.P.